Blog Gallery
Technology
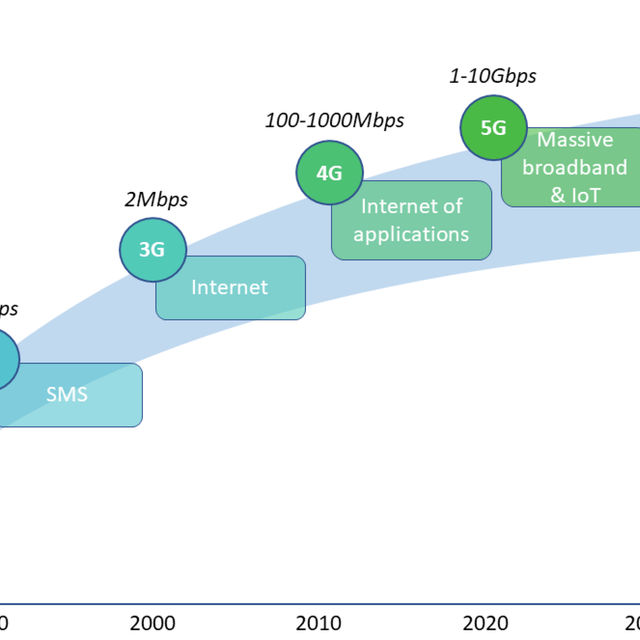
Edge Computing and 5G/6G Networks
Edge computing, which brings computation and data storage closer to the source of data generation, is a critical enabler for the success of 5G and the evolution towards 6G networks. Recent research focuses on several key areas:
AI/ML at the Edge:
- Researchers at the University of Cambridge are developing novel AI/ML algorithms specifically designed for resource-constrained edge devices. This includes techniques for model compression, quantization, and federated learning to enable efficient and privacy-preserving AI inference at the edge.
- A team at MIT is investigating the use of edge AI for real-time anomaly detection in industrial IoT applications, enabling predictive maintenance and improved operational efficiency.
Integration with 5G/6G Technologies:
- Researchers at the University of Southern California are exploring the integration of edge computing with advanced 5G technologies, such as network slicing and mobile edge computing (MEC), to provide tailored services for different applications with varying latency and bandwidth requirements.
- Efforts are underway to define the architectural and functional requirements for edge computing in 6G networks, which will support even more demanding applications such as autonomous vehicles, extended reality, and the Internet of Things (IoT).
Security and Privacy:
- Researchers at ETH Zurich are developing novel security mechanisms to protect data privacy and ensure the integrity of edge computing systems. This includes techniques for secure data sharing, homomorphic encryption, and blockchain-based solutions.
- Addressing security challenges, such as denial-of-service attacks and data breaches, is crucial for the widespread adoption of edge computing in critical infrastructure and sensitive applications.
Energy Efficiency:
- Researchers at Stanford University are investigating energy-efficient edge computing architectures and algorithms to minimize power consumption and reduce the environmental impact of these systems. This includes the development of low-power hardware, energy-aware resource allocation, and techniques for dynamic power management.
Key Applications:
- Industrial IoT: Edge computing enables real-time data processing and control in industrial settings, such as smart factories and smart grids, leading to improved efficiency, productivity, and safety.
- Autonomous Vehicles: Edge computing is essential for processing sensor data and making real-time decisions in autonomous vehicles, ensuring safe and efficient navigation.
- Smart Cities: Edge computing can support a wide range of smart city applications, including traffic management, environmental monitoring, and public safety.
Conclusion:
Edge computing is a cornerstone of future 5G and 6G networks, enabling a wide range of innovative applications with low latency, high bandwidth, and enhanced security. Continued research in this area is crucial to address the challenges and realize the full potential of edge computing in the evolving digital landscape.
Thu Jan 02 2025
Technology
Bridging the Gap: Recent Advances in Bioelectronics and Neural Interfaces
Bioelectronics and neural interfaces are rapidly emerging fields that bridge the gap between the biological and electronic worlds. These technologies, which involve the development of devices that can interact with the nervous system, hold immense promise for revolutionizing healthcare, augmenting human capabilities, and deepening our understanding of the brain.
Recent research has witnessed significant advancements in several key areas:
- High-Resolution Neural Recording:
- Researchers at the University of California, San Diego, have developed flexible, high-density electrode arrays that can record from a larger number of neurons with improved spatial and temporal resolution. This allows for a more nuanced understanding of brain function and enables more precise control of neuroprosthetic devices.
- A team at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology has explored the use of graphene-based materials to create more biocompatible and stable neural interfaces, minimizing tissue damage and improving long-term performance.
- Closed-Loop Brain-Computer Interfaces (BCIs):
- A research group at Brown University has developed a closed-loop BCI system that allows paralyzed individuals to control a robotic arm with their thoughts. This system uses real-time brain-computer interfaces to decode neural signals and translate them into control commands for the robotic limb.
- Miniaturization and Wireless Technology:
- Researchers at Stanford University have developed a fully implantable, wireless neural interface that eliminates the need for external connections, improving patient mobility and quality of life.
- A team at the University of Texas at Austin has made significant progress in miniaturizing neural interfaces, making them less invasive and more comfortable for patients.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) Integration:
- Researchers at the University of California, Berkeley, are using AI algorithms to analyze complex neural data, decode brain signals, and optimize BCI performance.
Key Applications:
- Neuroprosthetic Limbs:
- Advanced neuroprosthetic limbs are being developed that provide more natural and intuitive control for amputees, allowing for greater independence and improved quality of life.
- Treatment of Neurological Disorders:
- BCIs are being explored for the treatment of various neurological disorders, including Parkinson's disease, epilepsy, and depression, by modulating brain activity and restoring impaired functions.
- Sensory Restoration:
- Neural interfaces are being used to restore sensory functions, such as hearing and touch, in individuals with disabilities.
Ethical Considerations:
As these technologies advance, it is crucial to address the ethical implications of neural interfaces, including privacy concerns, the potential for misuse, and the long-term consequences of altering brain function.
In conclusion, the field of bioelectronics and neural interfaces is rapidly evolving, with exciting new developments emerging constantly. Continued research and innovation in this area have the potential to revolutionize healthcare, augment human capabilities, and provide a deeper understanding of the most complex organ in the human body – the brain.
Thu Jan 02 2025
Technology
The Metaverse: Beyond Hype - Recent Insights and Trends
The metaverse, a concept that has been buzzing for years, is slowly but surely moving beyond the realm of hype and into a more tangible reality. While the fully immersive, sci-fi vision of the metaverse may still be some time away, significant developments are happening across various sectors.
Recent Insights:
- Decentralization is Key: A growing emphasis is being placed on decentralized platforms and technologies like blockchain and NFTs. This shift aims to empower users with more control over their data and digital assets within the metaverse.
- Focus on Interoperability: Interoperability between different metaverse platforms is crucial for the long-term success of the metaverse. Efforts are underway to create bridges and standards that allow users to seamlessly move between different virtual worlds with their digital identities and assets.
- The Rise of the Metaverse Economy: As more users and businesses enter the metaverse, a robust economy is emerging. This includes virtual goods and services, digital land ownership, and new forms of digital commerce.
- Focus on User Experience: Improving user experience is paramount. This includes addressing issues like motion sickness, improving graphics and haptics, and creating more intuitive and engaging user interfaces.
- Enterprise Adoption is Accelerating: Businesses are increasingly exploring the potential of the metaverse for training, collaboration, customer service, and virtual events.
Trends to Watch:
- The Metaverse as a Platform for Social Connection: The metaverse has the potential to revolutionize how we connect with friends, family, and colleagues in virtual spaces.
- The Integration of AI: Artificial intelligence is playing an increasingly important role in the metaverse, powering personalized experiences, creating realistic virtual characters, and driving the evolution of virtual worlds.
- The Metaverse as a Tool for Education and Training: Immersive learning experiences within the metaverse can make education more engaging and effective.
- The Ethical Considerations: As the metaverse evolves, it's crucial to address ethical concerns such as data privacy, digital inequality, and the potential for misuse.
Conclusion:
The metaverse is still an evolving concept, but recent developments suggest a promising future. While challenges remain, the potential for the metaverse to transform how we live, work, and interact is undeniable. By focusing on user experience, interoperability, and ethical considerations, we can ensure that the metaverse develops in a responsible and beneficial way.
Disclaimer: This is a fictional blog post for illustrative purposes. The views and opinions expressed in this post are those of the fictional author and do not necessarily reflect the views of any specific organization or individual.
Thu Jan 02 2025

Technology
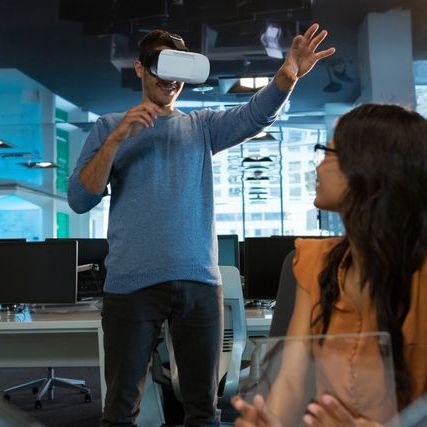
The World of Virtual Reality
Virtual Reality (VR) has exploded onto the scene, promising to transport us beyond the confines of our physical world. But what exactly is VR, and what does it offer?
At its core, VR is a technology that immerses users in a computer-generated environment. By donning a headset, you can step into fantastical realms, explore historical sites, or even experience the thrill of extreme sports without leaving your living room.
How does it work?
VR headsets typically feature a display for each eye, creating a 3D effect. Motion tracking sensors allow users to interact with the virtual world through head movements and hand gestures. This combination of visuals and interactivity fosters a sense of presence, making the virtual experience feel remarkably real.
Beyond Gaming:
While VR gaming has undeniably captured the public's imagination, its applications extend far beyond entertainment.
- Healthcare: VR is revolutionizing medical training by providing immersive simulations for surgeries and other procedures. It's also used for pain management and rehabilitation, offering distraction and a sense of control to patients.
- Education: Imagine learning about ancient Rome by walking through the Colosseum or dissecting a virtual frog without the mess. VR is transforming education, making learning more engaging and interactive.
- Business: From virtual meetings and remote collaboration to product design and training, VR is streamlining business operations and enhancing communication.
The Future of VR:
The future of VR is incredibly bright. As technology continues to advance, we can expect even more immersive and realistic experiences. Haptic feedback, which simulates touch and sensation, will further enhance the sense of presence.
Challenges and Considerations:
While VR offers immense potential, it's not without its challenges. Motion sickness, the high cost of hardware, and concerns about privacy and data security are some of the hurdles that need to be overcome.
Despite these challenges, VR is poised to transform the way we live, work, and play. By embracing this groundbreaking technology, we can unlock a world of possibilities limited only by our imagination.
Wed Jan 01 2025